Understanding Ductal Carcinoma: In Situ and Invasive Types
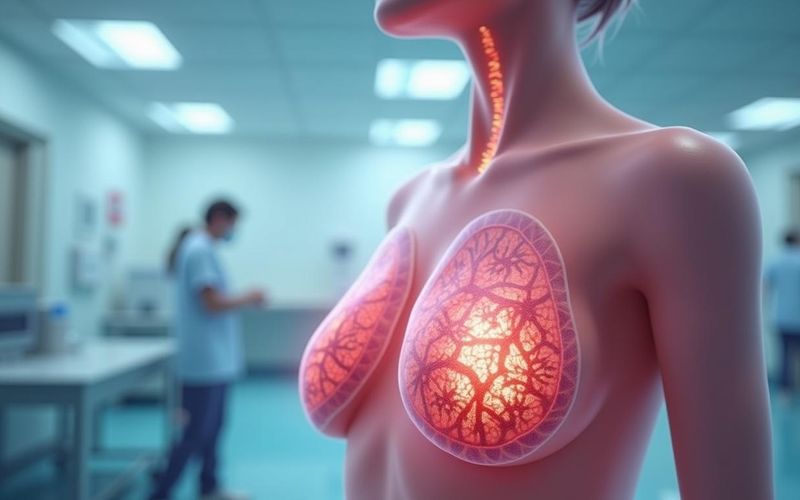
Ductal carcinoma is a type of breast cancer that starts in the cells lining the milk ducts. It can be classified into two main categories: Ductal Carcinoma In Situ (DCIS), which is non-invasive, and Invasive Ductal Carcinoma (IDC), which is more aggressive.
Treatment of Ductal Carcinoma In Situ (DCIS)
DCIS is highly treatable, often requiring surgical intervention. Treatment options include:
- Surgery: Options are Breast-Conserving Surgery (Lumpectomy) or Mastectomy, based on the extent of the disease.
- Radiation Therapy: Recommended after breast-conserving surgery to reduce recurrence risks.
- Hormone Therapy: Used for hormone receptor-positive cases to prevent future cancer.
- Observation/Active Surveillance: Evaluated in clinical trials for select patients.
Treatment of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma (IDC)
IDC is more aggressive and may spread beyond the breast. Treatment options include:
- Surgery: Lumpectomy or Mastectomy depending on the tumor's size and number.
- Radiation Therapy: Common after surgery.
- Chemotherapy: Used based on various prognostic factors.
- Hormone and Targeted Therapy: For specific tumor characteristics.
For both types, personalized treatment plans and participation in clinical trials are vital for effective care.